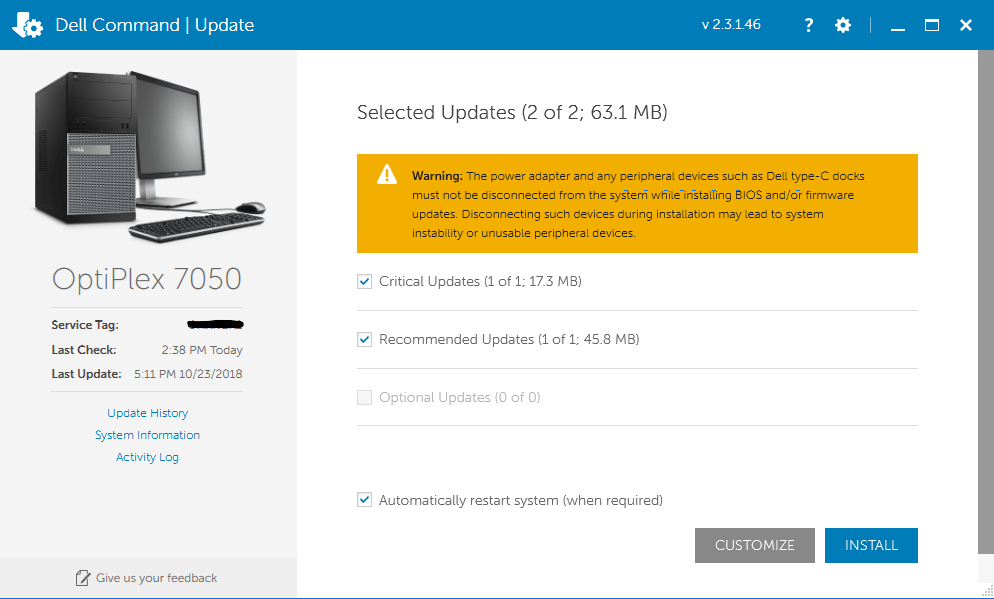
You may not know it, but your Dell computer comes with more than the operating system that you installed from the CD. Several other tools and programs are already on your computer. And one of these programs calls Dell Command Update. This tool is an essential part of your Computer’s overall health, and it can use to make sure that you have all of the most recent drivers and firmware updates on your Computer. Here are ten facts about Dell Command Update that you should know to use in the future correctly.
Dell command update
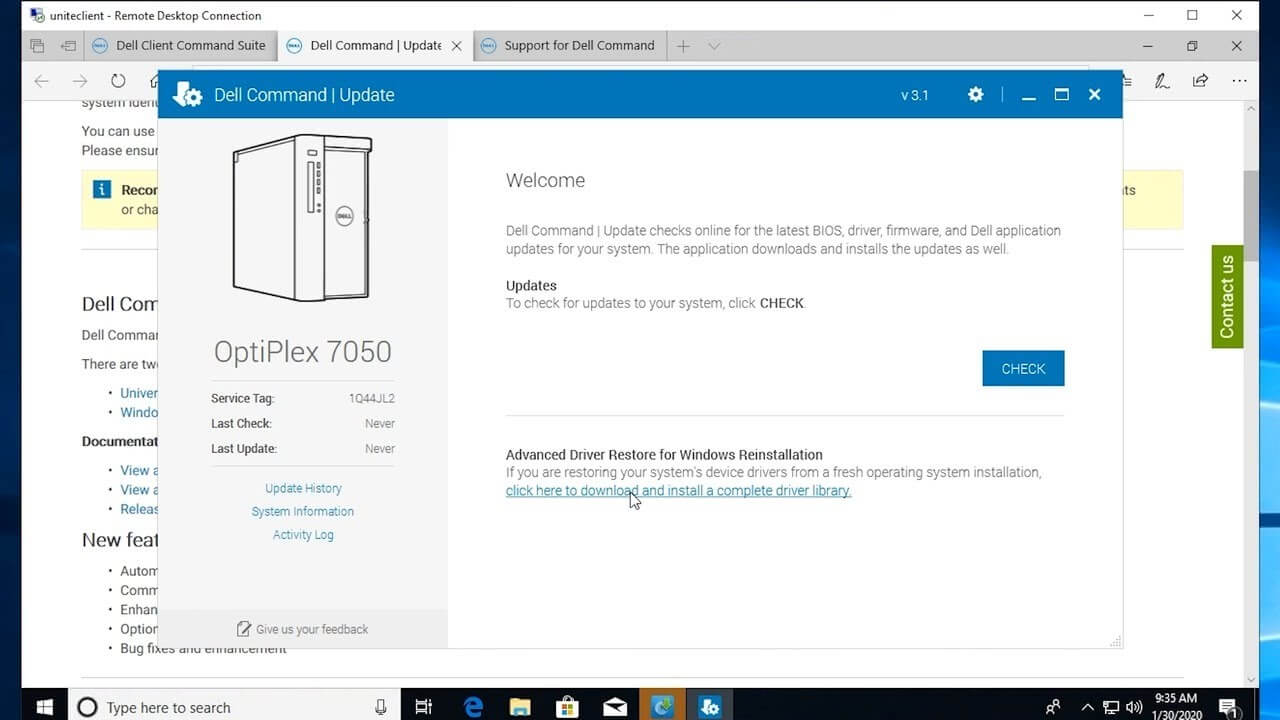
Dell command update is an application use to detect and download firmware for Dell computers. When you run Dell command update, it analyzes your system and downloads appropriate updates, if any are available. By default, you’re notified when updates are available but can opt-out of notifications and check for updates manually from within the Dell command update at any time. This application includes a built-in database of over 90 types of device drivers that support many different hardware configurations. If Dell command update detects a supported driver on your computer, it prompts you to install it. Dell command update also allows you to create a backup image of your hard drive or restore one. It’s important to note that the Dell command update does not provide technical support for Dell products; instead, it includes information about finding technical support elsewhere.
Should I update Dell Command?
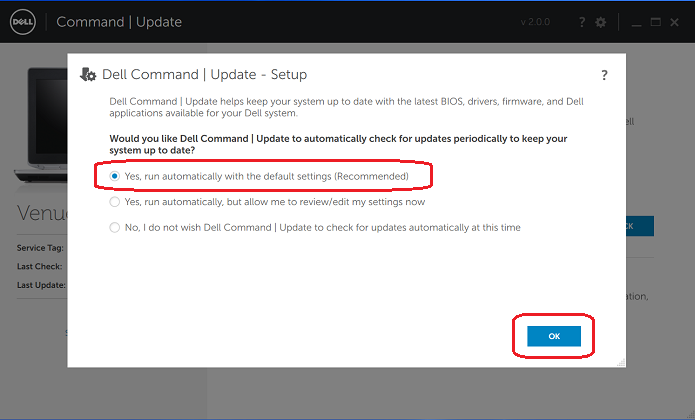
There is a new Dell Command Update 4.0, and it is available for download. But, should you update? 10 facts about Dell command update that might help you decide. Dell command update updates your existing copy of Dell command (Dell’s software for configuring and updating your system) to version 4.0, which gives you access to more configuration options than previous versions. Suppose your Computer update from Windows 7 or 8 to Windows 10. In that case, you are already using a newer version of Dell command than what ship with your computer and have not needed an upgrade. So you probably don’t need to do anything here.
If you haven’t installed Dell command on your computer yet, you can install Dell Command Update 4.0 now. Dell command update will tell you if there is a newer version of the Dell command available but only if you connect to Dell Support – So, be sure to check in with them regularly. The best way to get support from Dell is by calling their phone number or connecting online via chat if there are any issues after installing Dell Command Update.
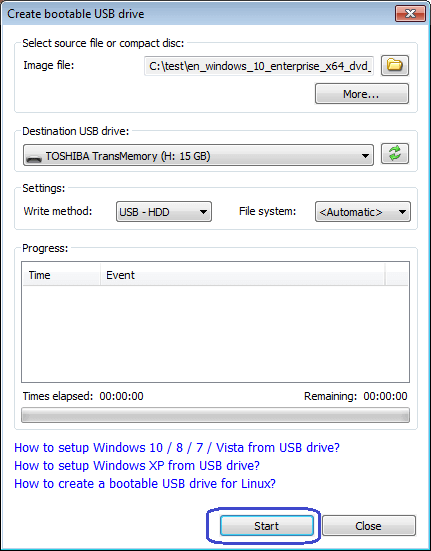
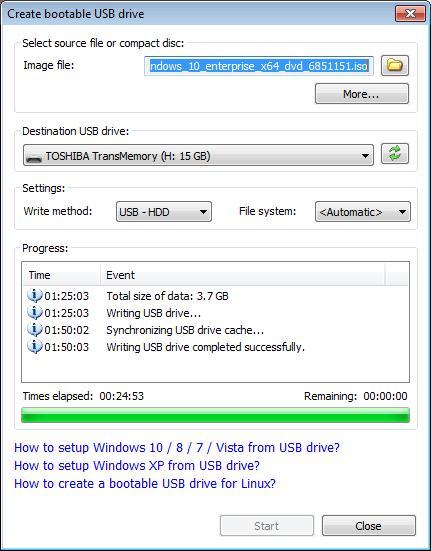
1) Set up a bootable USB
Setting up a bootable USB drive is necessary to use Dell Command Update. This process varies slightly depending on your operating system and whether or not you already have a bootable OS in place. Likely, you won’t need all of these steps, so choose those relevant to your situation. First, make sure your USB drive is formatted as either FAT32 or NTFS; it should be no larger than 32GB and only contain data that can be lost. On Windows 8, hold down Shift+F10 while right-clicking on Computer, then select Manage to launch Computer Management.
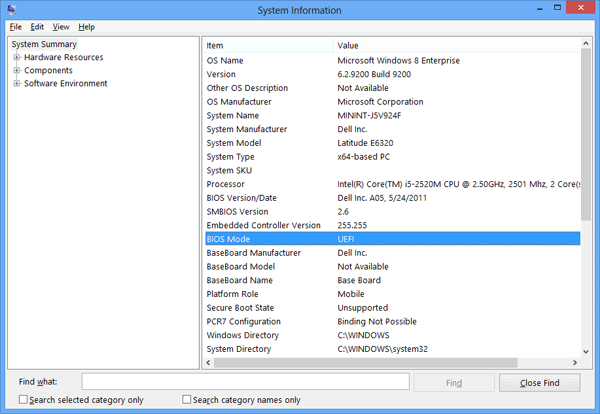
2) Check if your system supports UEFI
Dell Command Update 4.0 does not work on legacy BIOS systems. It’s essential to check your system’s support for UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). UEFI is a new style of firmware that replaces legacy BIOS firmware in PCs and servers. You can determine if your system supports UEFI by checking your manufacturer’s specifications or looking in Windows Device Manager under System Devices. If you see UEFI, it supports UEFI; if you see only BIOS, it doesn’t support UEFI. To check your device, right-click on Computer in File Explorer, select Properties, select System Information, and look at Boot mode. Boot mode indicates how Windows starts up from power-on: Legacy BIOS: When set to Legacy BIOS, the computer boots up using Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware.
3) Download and save your drivers
One of your biggest enemies as a computer user is inactivity. Over time, your drivers get out of date, leading to hardware and software incompatibilities. The easiest way to prevent hardware issues is to update your system’s drivers frequently. Drivers are little pieces of software that tell programs how to work with various amounts of hardware—your video card, sound card, network adapter, etc. While you can manually dell command update download driver updates from manufacturers’ websites.
It’s best to use an automated tool like Dell Command Update. This handy utility automatically checks for new versions of your drivers and downloads them when they’re available. Once you install these updates, you’ll be able to run more recent programs on your PC without running into problems or experiencing glitches because of outdated hardware support. It’s also important to keep track of which version numbers correspond with which operating systems to know what kind of software will work on your machine.
4) Find which drivers you need
The first step to using Dell Command Update is figuring out which drivers you need. Head to your PC manufacturer’s website and look for a download section (usually under support or drivers). Once you’ve downloaded it, launch it and check if any of your hardware needs updating; note which driver it was and move on to downloading from either Intel or AMD. If none of your hardware requires an update, you’re ready to install DSU.
5) Get ready to install
First, close all your open applications and connect to your system with an Ethernet cable. Next, perform a cold reboot of your server. Turn off power to the unit by pressing down its power button for about five seconds. Then turn it back on again by pressing down and holding it for three seconds. Let it boot entirely before moving on to downloading from Dell’s site. You’ll need to download two files: The first one is dell cmd update, which is labeled DDCUWIN-BXX, where XX varies by system architecture (either 32 or 64). Downloading will give you installers for both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows.
The Review Of Alienware Area51 Threadripper Edition
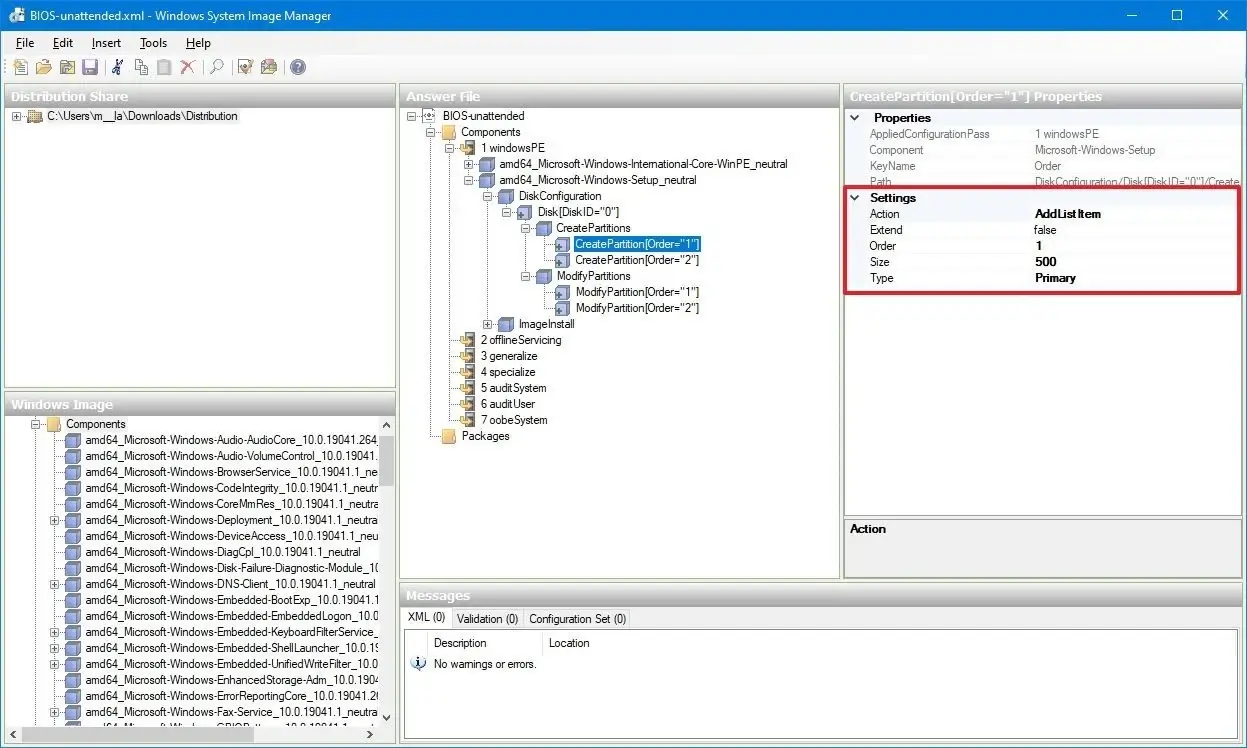
6) Create an unattended answer file
When you need to deploy a system image or drivers, you can do so by manually loading drivers and other components after deploying Windows. But most administrators find it easier to create an answer file with all of these components listed and pre-loaded. An answer file is simply a text file that Windows reads as it boots up. You can store an answer file in a shared network location or on a removable drive, then boot your systems using PXE booting to automatically deploy them over the network. The easiest way to create an answer file is by using Windows System Image Manager (WSIM), included in both Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT) 2013 and Microsoft Assessment and Planning (MAP) Toolkit 2013.
7) Install your software
Unlike Windows, where you have to install your software from a disc, in Ubuntu, you download it directly. To do so, search for each program online and download it from Ubuntu Software Center. Once it’s downloaded, click on Install and wait for Ubuntu to finish downloading and installing it for you. Some programs may need extra dependencies that are required before running correctly. If that’s true for a particular program, you’ll be prompted during installation. If there are no issues during installation and everything is as expected, move on to your next program. Otherwise, head back to Ubuntu Software Center and try downloading again. Repeat until all of your programs are installed.
8) Reboot into the flash tool environment
Boot your Computer from an external device. Insert a dell command update for windows 10 flash drive into a USB port, restart your computer, and press F12 to access boot options. Choose your flash drive, and then select UEFI: Flash BIOS mode to reboot into a specialized utility for updating BIOS. Select BIOS Setup to launch a utility for modifying hardware settings such as system time, video resolution, and boot order; you can also use it to update BIOS from within Windows 10 if you prefer. You should download and install Dell Command Update (DCU) first to start with driver updates on your PC running Windows 10. OEMs and enterprises use DCU to customize their systems based on their needs before shipping them out.
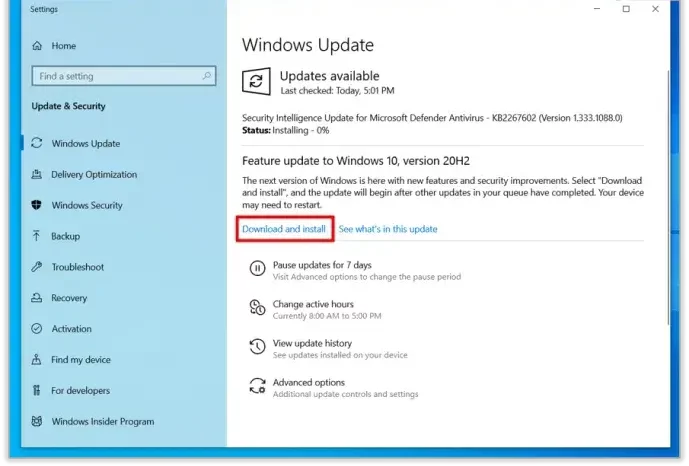
9) Run CSU.exe to update your computer
Usually, you won’t need to use Command Update yourself; it runs automatically behind the scenes whenever you update your Computer through Windows Update. To access it, if you do want to run it manually, search for Command in your Start menu, then click on Command Prompt. In Vista or Windows 7, right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as Administrator. Now type c: behind the scenes \dell\drivers\scs download and press Enter. In XP or 2000, type cd c:\delldriverdownloads, then press Enter. Follow the prompts on the screen, and you should be set.
10) Final steps to do a complete installation
This final set of steps is recommended only for dell command-branded Operating Systems that are not bootable. During installation, you will be presented with several choices for drivers, network settings, and user accounts. It is recommended that you follow the Wizard. If, however, you would like to customize your configuration more precisely, you can follow these steps instead: Connect your Computer to a power source before starting. Power on your computer and allow it to boot completely into Windows. Ensure you do not get any error messages during or after starting Windows (particularly those referring to missing drivers). Open Device Manager by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del keys together or right-clicking My Computer and selecting Manage.