The term that Google gave its doodle, the fossil is more commonly known as “Turkana Boy. A group of archaeologists working in the Turkana region of Kenya unearthed a three-million-year-old skull and partial skeleton that would turn out to one of the most important finds in human history. Who found Turkana Boy? This special Google Doodle celebrates the groundbreaking work that helped answer this question and provided an interactive learning opportunity for people worldwide to learn about this important archaeological site! If you’re curious about the who, what, when, where, why, and how of this new doodle, you’ve come to the right place! Here are some quick facts about turkana human.
Who is a Turkana human?
Turkana human, the hominid fossil found in Kenya and believe to be about 1.5 million years old, is honore in this search engine’s celebration of Eart. The earliest famous ancestor of man, the Turkana boy, is celebrate as an icon for global climate change as one of the first humans to adapt to environmental challenges from water scarcity and periods of intense heat. His discovery means that not only are there more than 7 billion people living on earth today, but a vast number of other early human species have co-existed with us at some point over the last 3 million years.
The National Geographic Society acquire the Turkana boy and place him under UNESCO protection until his remains were return to Keny. The society commissioned artist Ann James to create the illustration for google doodle digs into the turkana human Earth Day. The story of the Turkana boy skull has been told many times because it represents so much about who we are and where we come from? Remember that even though we’re all human, but differences matter – diversity is what makes life interesting. Taking care of our environment now will provide sustainable resources for future generations (humans) like Turkana boy – something worth celebrating!
What Makes Discovering a Turkana boy So Exciting?
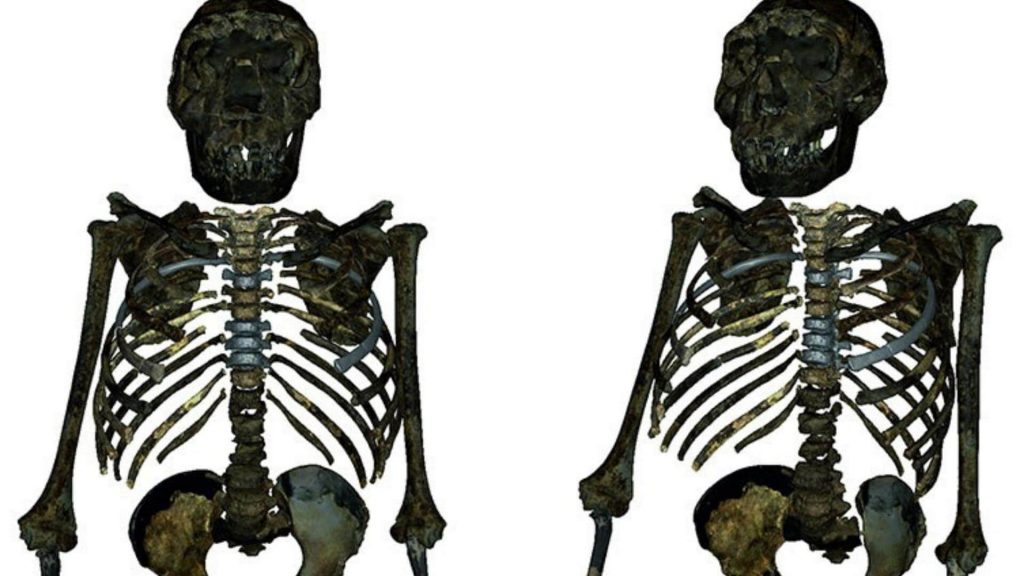
Turkana boy skull is one of the oldest souls on earth. He has a nearly complete skeleton with very few missing bones. Scientists are still study him to learn more about human evolution. And how it relates to other hominids living in this region, like Homo erectus. The fossil record shows us that our ancestors lived in Africa 2 million years ago. We are still trying to figure out how they got there. And why they stay put while their cousins move worldwide.
The climate shift from lush green rainforest to dry savannah as humans change their lifestyles from hunter-gatherers to herders. Which makes sense because you can’t hunt without water! Therefore, it celebrates the Turkana human. And as they grew more dependent on animals for food, they started moving around and spreading across East Africa. The fossils suggest that all ancestors come out of eastern Africa. But there’s a mystery surrounding when they left and why. Some of them may have migrated north or south during ice ages and return when things warmed up again. While others died off and were replace by new species that migrate out of Africa.
What is significant about Turkana Boy?
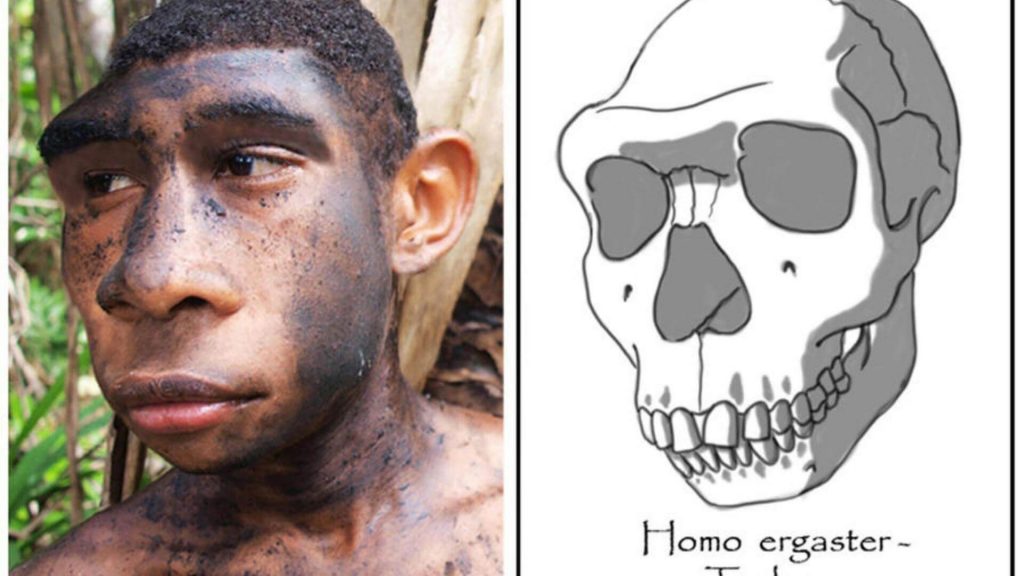
The discovery of Turkana boy! The more like Turkana boy google doodle celebrates the google doodle turkana human as one of the most strik examples of our ancestral roots. The sketch artist, Mari Matsumoto, drew on various reference materials to accurately portray this historic discovery. He was found by Kamoya Kimeu, Bernard Korir, and Richard Leakey during an expedition to Lake Turkana. Turkana Boy identifies as Homo erectus, and evidence suggests he live some years ago. Which is consider the oldest known fossil of Homo sapiens ever find. More importantly, it’s evidence that provides clues to the evolutionary transition from Homo erectus to H. sapiens.
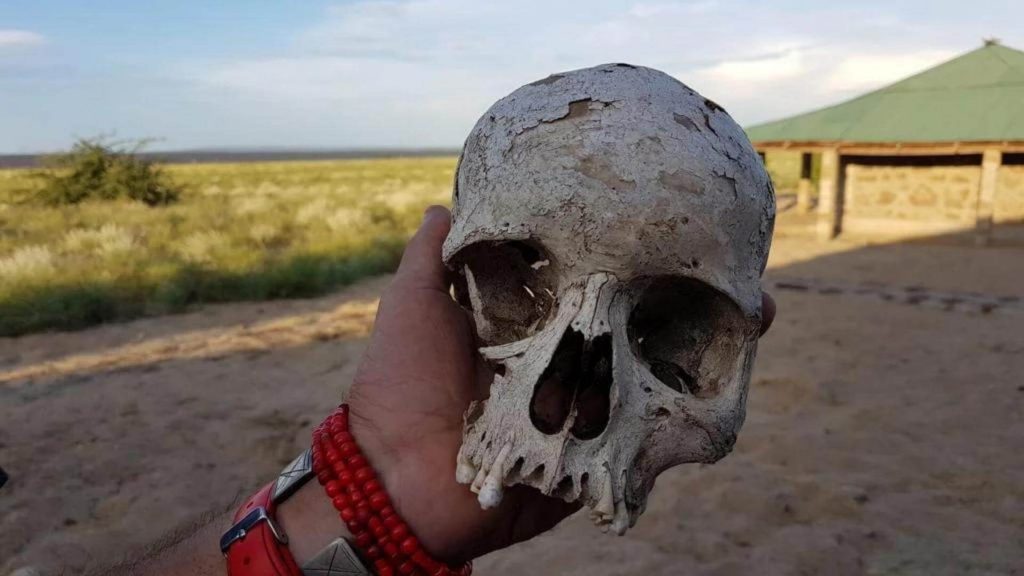
Such as those belonging to Australopithecus afarensis and Kenyanthropus platyops (uncovered at Lake Turkana). His name derive from his place of discovery: Lake Turkana, Kenya. His significance lies in his age and how well-preserve his remains are, enable scientists to examine them thoroughly. And who found Turkana boy? There’s no question that the more like Turkana boy google doodle celebrates the importance of find. And preserve what we find today for future generations to appreciate. Turkana boy among many artefacts studied, explore. And research so people will continue to learn about him. What he may mean for us all. And how important it is not only to learn from him but also to preserve him to ensure future generations can also celebrate with us.
Why is Turkana famous?
Well, he called the close thing to a Neanderthal we’re ever to find. He was found on the banks of Lake Turkana in Kenya. For years, scientists have tried to unlock the secrets of his genetics and who he might have encounter. The mystery continues as they can’t figure out why he has such a small skull when his body is so tall. They are sure that he died sometime between 8 and 13. One day, there may more answers, but we celebrate him, and the day he discover.
Turkana human google doodle name is unknown because nobody knows where he came from or how old he was when he died. However, we know he lived near a lake and made stone tools like other humans at that time. Nowadays, we still try to figure out where his family tree is. And if anyone else who shares similar traits with him lives nearby. Until then, it’s an exciting journey of discovery to understand the past from one person’s bones and teeth!
Interesting Facts About the Turkana Human
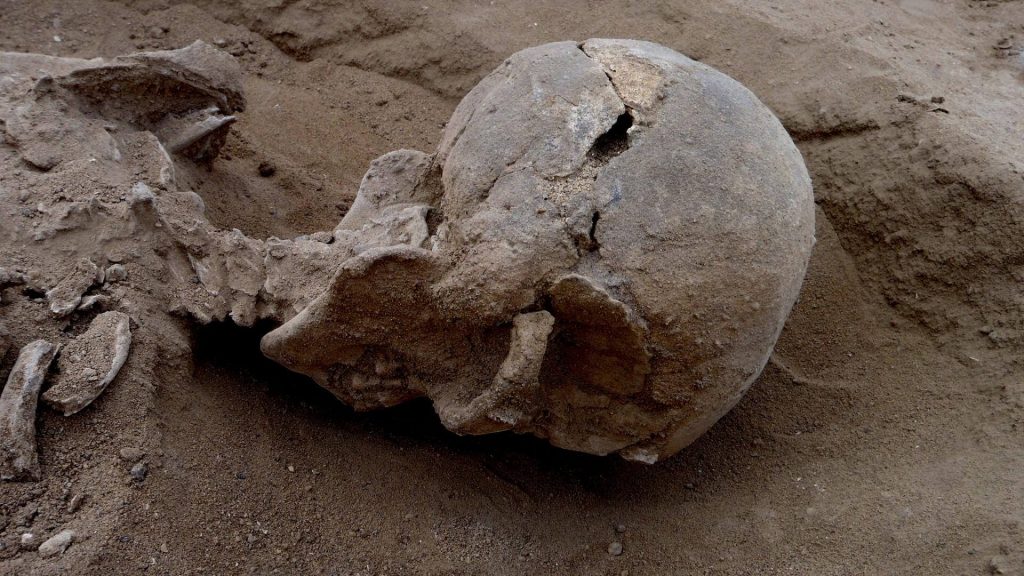
The Fossil Was Discover in Kenya, Turkana BoyThe fossil is one of several discover at Lake Turkana, Kenya, hence its name, according to National Geographic, which says it’s sometimes called “Turkana Boy. It discovers and was about 1.5 million years old. This was a human Erectus and is famously known as ‘Turkana Boy,'” report National Geographic. There were other fossil discoveries at Lake Turkana. According to Britannica, several “important fossils’ ‘ were unearthe along the shores of Lake Turkana, in what is called the “Koobi Fora sites. One was scientifically called an Australopithecus anamensis. And push back the of “bipedalism” walk on two legs and feet.
The Turkana Human was a Male Child
According to the Smithsonian, the skeleton allows scientists to find out a lot of information about body size, body shape and growth rates of Homo erectus. One key factor is that the seleton is 40% complete. Smithsonian report that the skeleton was a male, as determin by his pelvis, and he was only 8 or 9 years old. This skeleton is 40% complete. Base on the principle that bones from one side of the body can tell what the same bone from the other side looks like even if it’s missing,” according to the Smithsonian. “He was 1.6 m (5 ft 3 in) tall and weigh 48 kg (106 lb) when he died; if he had reached adulthood, he might have grown only a little bit taller,” the Smithsonian reports.
Turkana Boy Could Probably Hunt & Throw
We can glean details about the lives of early humans through Turkana Boy. According to BBC, he and his family probably could carry hunting tools, such as spears, due to their hands. One study found that they could throw and hunt, which were progressions from more ape-like ancestors, BBC reported. Some people question why Google labels the Doodle “Turkana Human” when the fossil is more commonly called Turkana Boy. “Wonder why they said turkana hum instead of Nariokotome Boy or Turkana Boy? I’m curious about the choice,” wrote one woman on Twitter.
If you look at it in a certain way, it’s not an issue, commented another person. The boy lived in what’s now Kenya but was never a Kenyan citizen. He would have been part of the Turkana tribe that lives there today. Though there were other tribes around him, a human would be appropriate for anyone who lived back then. It’s unclear if this was intentional, but Turkana (also spelled Turakina) means people.
How was the Age Of Turkana Boys Assess?
Whether the teeth or skeletal maturity stage chose. And if that maturity compare to that of Homo sapiens or chimps, then estimates of the death age different. The teenage growth surge that contemporary humans experience is not present in chimpanzees. However, it is possible to establish that he died around age 13. Establishing his exact age is more complicated, and estimates range from 8 to 17 years old. Richard Leakey’s team discovered the Turkana boy (Homo erectus) in West Turkana, Kenya. In their search for hominid fossils, they found an almost complete skeleton of an adolescent boy killed by a wild animal. It turnedout that these were the remains of one of the most important fossils finds ever made – known as Turkana Boy. And one which enable scientists to make great strides in understand human evolution.